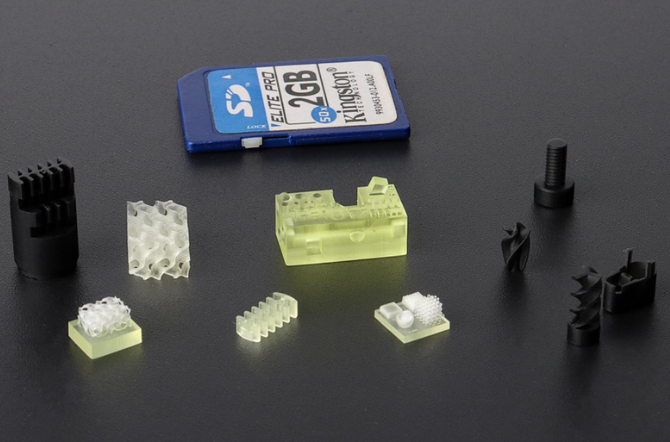
A Brief into Micro 3D Printing.
Micro 3D printing, also Micro AM, is a micro-fabrication technique that allows the design of very small sizes, at the micrometer scale and below, particularly popular in the electronics industry. It is growing steadily, due to the surging demand for miniaturized devices in electronics, biotechnology, automotive etc.,
Micro AM generally refers to the production of parts measured in single-digit microns down to a layer thickness of 5 microns and a resolution of like 2 microns. While if we look at the regular, more well-known resin 3D printing technology solutions on the market, like Formlabs Form 4, the pixel size is 50 µm. Micro AM shows 10 time more resolution in presenting details.
Most micro 3D printing is accomplished through resin printers, or more specifically, photopolymerization reactions with light. Some companies, however, have begun moving beyond polymers and into the realm of metals, including steel, copper, and gold. Let’s take a look at the major categories of micro-additive manufacturing technology.
Technologies of Micro 3D Printing includes:
| Technology | Material | Min. Resolution | Layer thickness | Application |
| Microstereolithography (µSLA) | Resin | 5µm | 5-50 µm | Microfluidics; Micro-optics, Biomedical microdevices |
| Projection Microstereolithography (PµSL) | Polymer, biomaterials, ceramics | 2µm | 5-50 µm | Microfluidics; Tissue engineering; Micro-optics, Biomedical microdevices |
| Two-Photon Polymerization (2PP or TPP) | Resin,silica nanocomposite, hydrogels | 0.1µm | 0.1-5.0 µm | Tissue engineering; Medical implants; Micromechanics |
| Lithography-based Metal Manufacturing (LMM) | Metal powder | 35µm | 10-100µm | Surgical tools; Micromechanical parts |
| Electrochemical Deposition | Metal liquid | <1µm | NA |
|
| Micro Selective Laser Sintering (μSLS) | Metal powder | <15µm | 1-5 µm | Surgical tools; Micromechanical parts |
|
Applications of Micro AM covers:
- Electrical components
- Microchip components
- Microfluidic devices
- Drug-delivery microneedles
- Vascular stents
- Micro-scal molds
- Electro-mechanical parts for optics & photonics
Micro electromechanical systems (MEMS)
Micro AM vs. Traditional methods
Traditional manufacturing methods, like microinjection molding, mocromachining, etching, can produce tiny parts, while these processes can be complicated and expensive when it comes to single or small batch items. Micro AM provides an alternative to the customization for miniaturize structures.
Micro AM technology is not as a replacement for micro injection molding presently, but a complement to existing manufacturing processes. The incorporation of this technology to design and manufacture micro injection molds and tooling, for example, generates great value in the form of optimizing final part design and reducing time to mass production.
Reduce manufacturing lead times. 3D printing technology can directly convert designed models into physical objects, eliminating multiple steps and processes in traditional manufacturing, significantly reducing production lead times and improving manufacturing efficiency.
Higher precision, increased part complexity. Micro AM can reduce the overall external dimensions the design, and also frees the design complexity.
SteraFab is pushing the limits of micro 3D printing by offering prototype and production volumes of micro-sized parts, rapid tooling for micro injection molding, and developing novel solutions to customer problems utilizing Micro AM technologies.A Brief into Micro 3D Printing.